Cor Pulmonale Treatment Guidelines
Cor pulmonale treatment guidelines. ESC Clinical Practice Guidelines aim to present all the relevant evidence to help physicians weigh the benefits and risks of a particular diagnostic or therapeutic procedure on Pulmonary Hypertension. Onset of cor pulmonale. Cardiopulmonary support for patients experiencing acute cor pulmonale with resultant acute RV failure includes fluid loading and vasoconstrictor eg epinephrine administration to maintain.
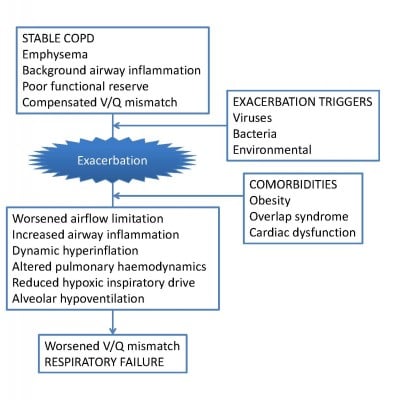
Inasmuch as the cardiac involvement is rooted in the underlying pulmonary dysfunction therapyif it is to be successfulmust be directed at both pulmonary and cardiac aspects of the disease. Ask your healthcare provider how much liquid you should drink each day. The diagnosis of cor pulmonale heart disease secondary to lung disease calls for close cooperation between the chest physician and the cardiologist.
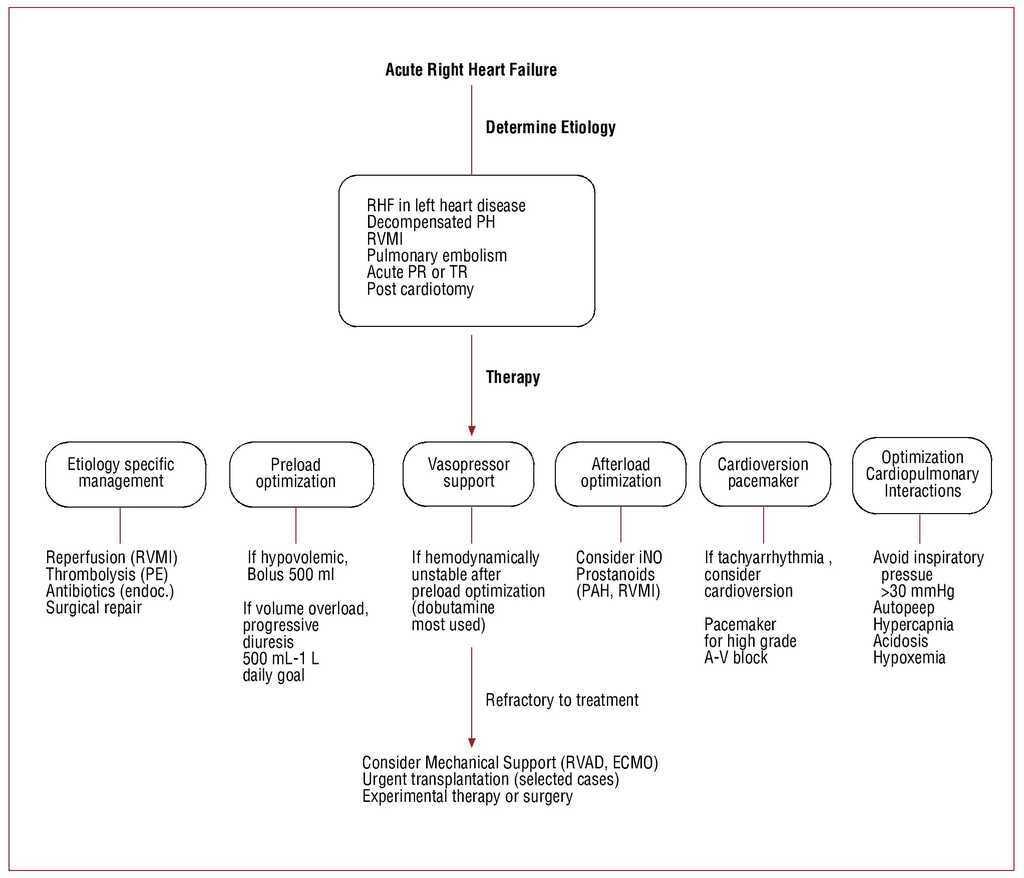
This has limited our therapeutic approach in this form of chronic cor pulmonale to rigorous restriction of physical activity directed at minimizing exacerbations of pulmonary hypertension. Treating cor pulmonale Ensure that people with cor pulmonale caused by COPD are offered optimal COPD treatment including advice and interventions to help them stop smoking. How can I manage my cor pulmonale.
Pulmonary vasodilator compounds should be used with caution because they can compromise gas exchange in cor pulmonale from secondary pulmonary hypertension. Without heparin prophylaxis 84 of patients will have pulmonary thromboembolism after hip or knee replacement. Treatment strategies for cor pulmonale include supplemental oxygen assisted mechanical ventilation digoxin and diuretics.
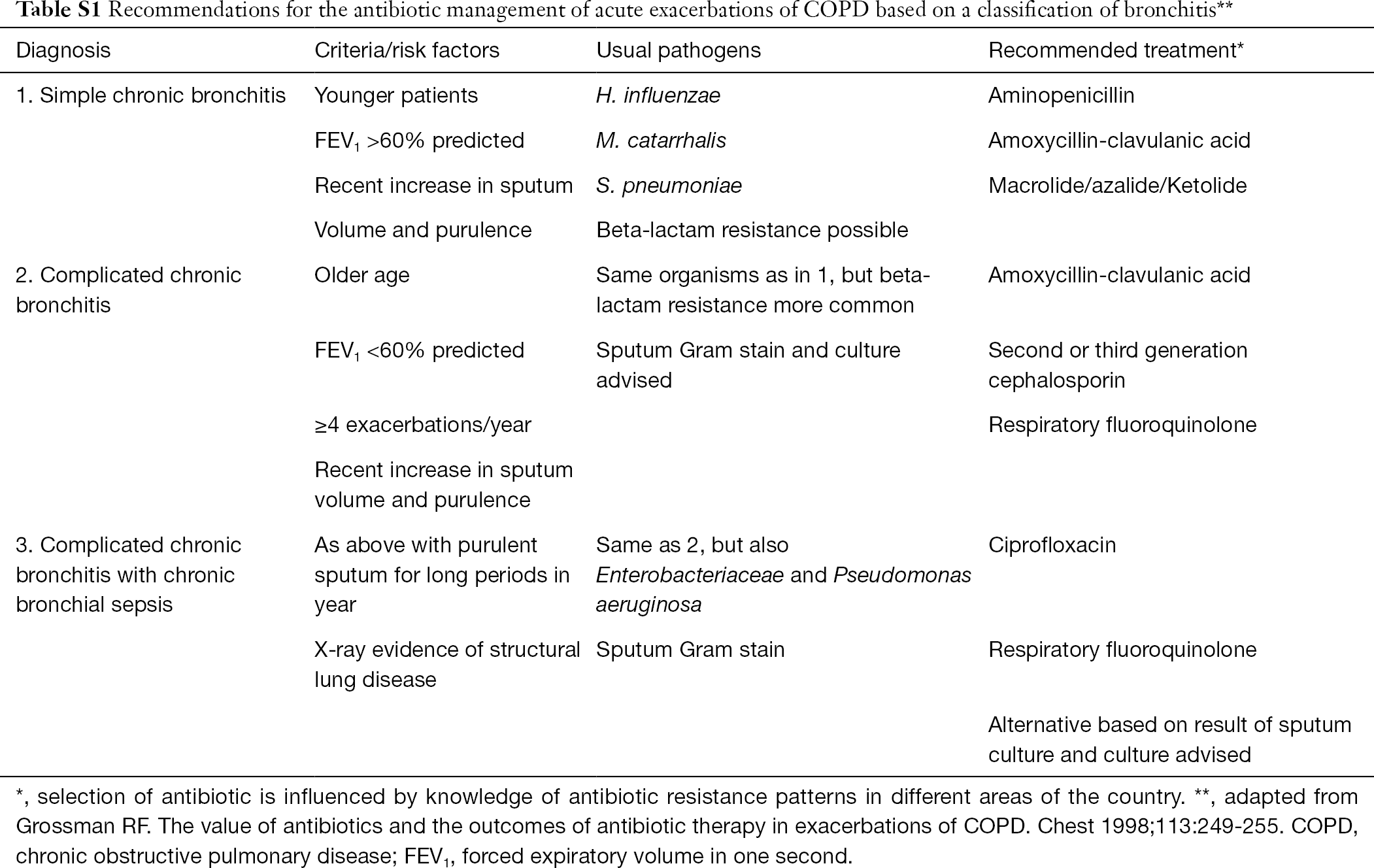
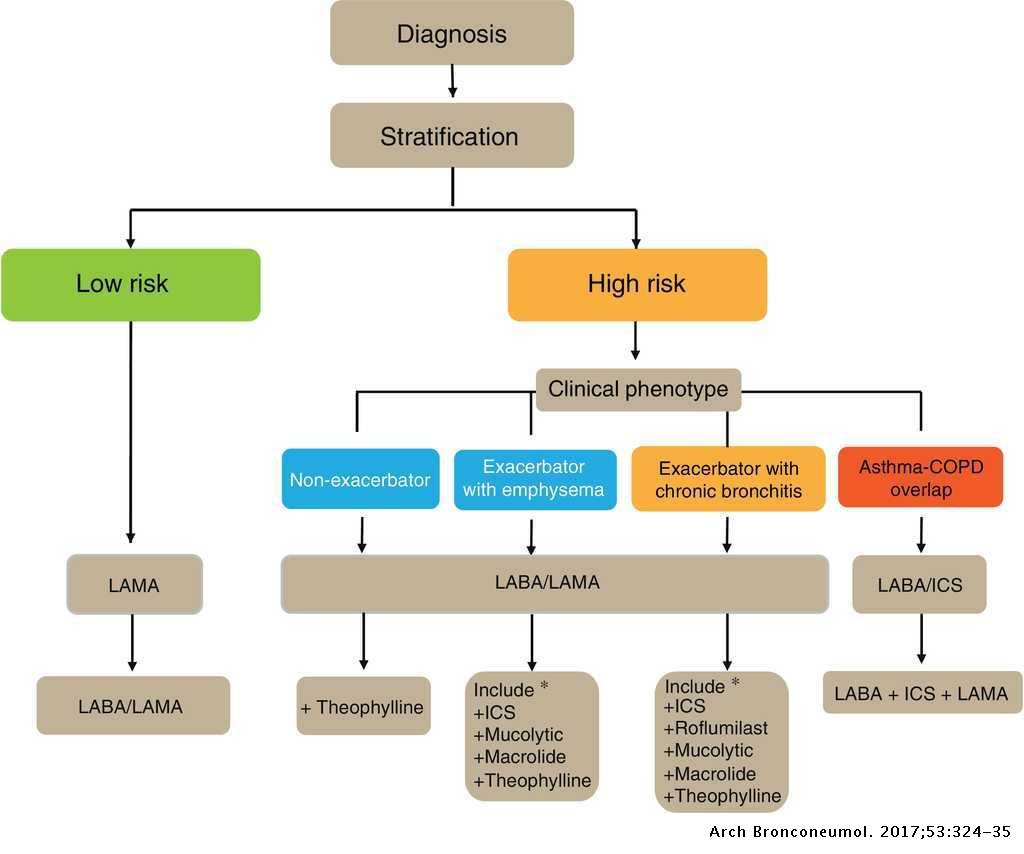
Justify need for continued treatment or supervise withdrawal. Overview of treatment shown in Table 124-1. If this problem persists please contact Technical Support for assistance.
Monday-Friday 8 AM - 9 PM ET -5 GMT. Pulmonary embolization is the most common preventable cause of death in hospitalized patients. Notably ACE inhibitors and beta blockers are cornerstones of therapy in pts with HFrEF.
Optimise therapy and measure blood gases. For people who need treatment for hypoxia see the section on long-term oxygen therapy.
Onset of cor pulmonale.
Ask your healthcare provider how much liquid you should drink each day. Particular emphasis will be placed on chronic obstructive pulmonary dis-ease COPD which is by far the main cause of cor pulmonale. We apologize for the inconvenience. Too much liquid can increase your risk for swelling and make your cor pulmonale worse. Limit your liquids as directed. Trials with digoxin and inotropic agents have been evaluated. Justify need for continued treatment or supervise withdrawal. This typically presents with swollen ankles and lower legs. You may need to change what you eat to control your symptoms.
While emphasis has been placed upon the difference in management of the patient with emphysema or fibrosis and cor pulmonale nonetheless it should be remembered that in any individual patient these two. For people who need treatment for hypoxia see the section on long-term oxygen therapy. Association for European Paediatric and Congenital. This has limited our therapeutic approach in this form of chronic cor pulmonale to rigorous restriction of physical activity directed at minimizing exacerbations of pulmonary hypertension. The diagnosis of cor pulmonale heart disease secondary to lung disease calls for close cooperation between the chest physician and the cardiologist. Phlebotomy during hypoxic cor pulmonale has been suggested but the benefits of decreasing blood viscosity are not likely to offset the harm of reducing oxygen-carrying capacity unless significant polycythemia is present. Ask your healthcare provider how much liquid you should drink each day.




































Post a Comment for "Cor Pulmonale Treatment Guidelines"